McKinsey article covers key benefits of tokenization

(Image Source)
GLOMcKinsey article covers the basic benefits of tokenisation. Read in full
Key takeaways:
- Despite recent high-profile criminal cases, companies across various industries, including financial services, retail, music, gaming, and media, are actively exploring opportunities within Web3, such as tokenized loyalty programs.
- In the financial services sector, there is a growing focus on the resurgence of the “blockchain, not crypto” narrative, with banks, asset managers, and other institutions showing keen interest in the technological potential of tokenization.
- Tokenization involves creating digital representations of traditional assets on a typically private blockchain or distributed ledger. Numerous leaders of major institutions have publicly expressed their fascination with how tokenization could revolutionize capital markets.
- Analysts predict that between $4 trillion to $5 trillion worth of tokenized digital securities could be issued by 2030, and there are already significant real-world examples in production. For instance, Broadridge, a US-based fintech infrastructure company, facilitates monthly tokenized repurchase agreements worth over $1 trillion on its Distributed Ledger Repo (DLR) platform.
- Process of tokenisation – tokenization involves the creation of digital tokens on a blockchain that represent various types of assets, including physical assets like real estate, agricultural or mining commodities, and analog artworks, financial assets such as stocks and bonds, as well as intangible assets like digital art and intellectual property. This process typically includes four fundamental steps.
Tokenization grants asset holders and market participants access to the advantages offered by blockchain technology, which encompass continuous operations, data accessibility around the clock, and immediate settlement, referred to as “atomic settlement.” Additionally, tokenization provides programmability, allowing code to be embedded in tokens and enabling them to interact with smart contracts, leading to increased automation.
Key benefits of tokenization:
-
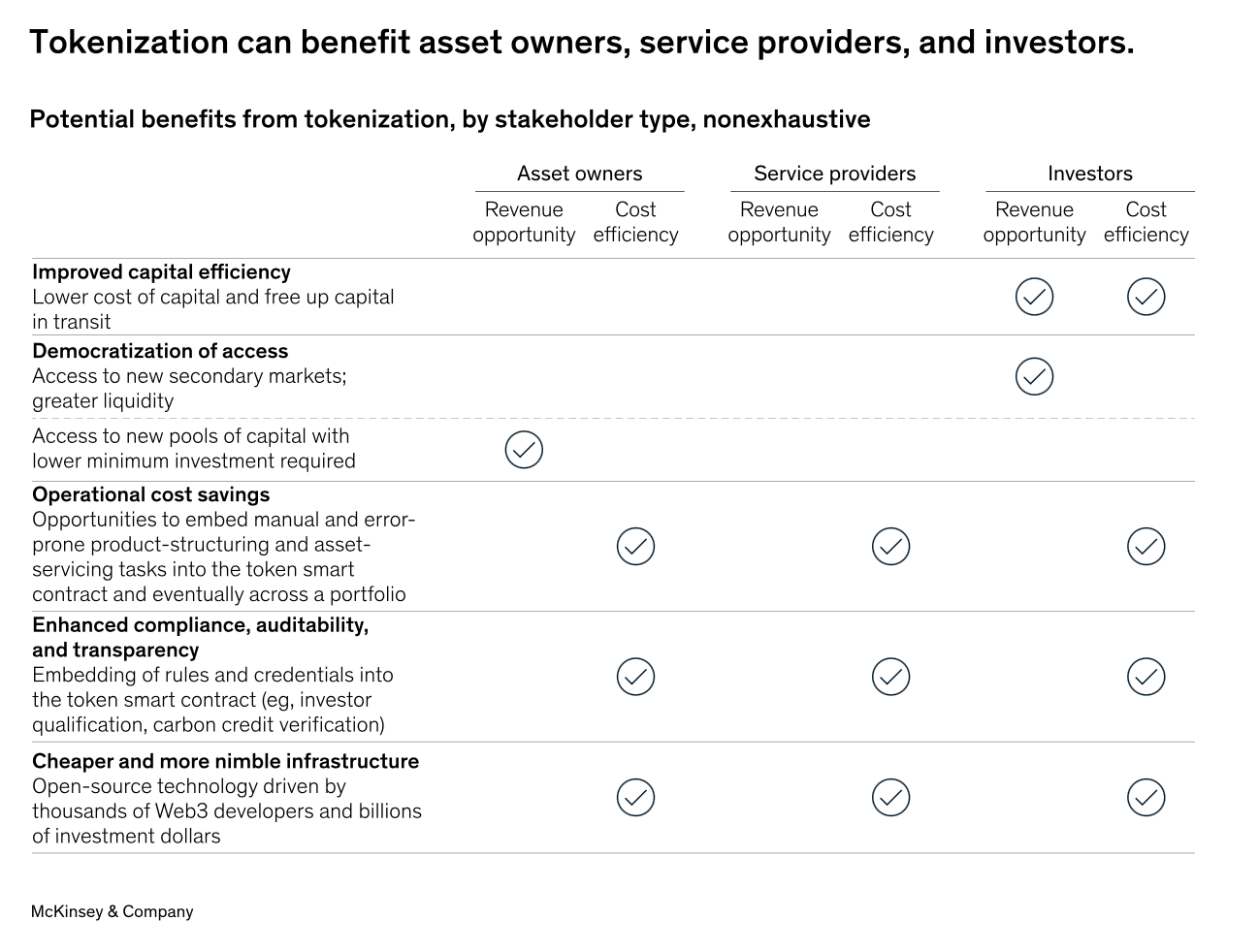
Enhanced Capital Efficiency: Tokenization can significantly improve capital efficiency in specific capital market scenarios. For instance, it can reduce the settlement time for transactions like tri-party repurchase agreements or money market fund redemptions from the current T+2 standard to a matter of minutes. These shorter settlement times can result in substantial cost savings, especially in high-interest-rate environments.
-
Democratization of Access: One of the prominent benefits of tokenization is the potential for democratizing access, achieved through fractionalizing ownership into smaller parts. This streamlining can make it economically feasible to serve smaller investors in some asset classes. However, regulatory restrictions may limit access to tokenized assets to accredited investors, and true democratization of access will require broader adoption.
-
Operational Cost Savings: Asset programmability can yield cost savings, especially for asset classes with manual, error-prone processes and numerous intermediaries. Tokenized assets can automate functions like interest calculations and coupon payments through smart contracts, reducing their costs. Smart contract automation can also lower the cost of services such as securities lending and repos and offer portfolio-level benefits by enabling real-time rebalancing by asset managers.
-
Enhanced Compliance, Auditability, and Transparency: Tokenization can automate compliance checks by embedding specific compliance-related actions into tokenized assets. This results in streamlined compliance checks and reporting, immutable record-keeping, and real-time, auditable accounting. For example, in carbon credits, blockchain technology can provide a transparent record of credit purchase, transfer, and retirement with built-in functionality for transfer restrictions, measurement, reporting, and verification.
-
Cost-Effective and Agile Infrastructure: Blockchains are open source and continuously evolving, driven by Web3 developers and substantial venture capital investments. Assuming financial services firms choose to operate private or hybrid instances of public permissionless blockchains, they can readily adopt future innovations in areas like smart contracts and token standards, further reducing operating costs.
(Image Source)
-
Source: McKinsey




